This post was imported from the Open Distro For Elasticsearch blog, a predecessor project of OpenSearch. Information reflected in this post may not be current or accurate.
Open Distro for Elasticsearch is a popular choice for use cases such as log analytics, search, real-time application monitoring and click-stream analysis and more. One commonality among the various use cases is the need to write and run queries to obtain search results at lightning speed, and that in turn, requires the user to have expertise in the JSON based Elasticsearch query domain-specific language (Query DSL). Although Query DSL is powerful, it has a steep learning curve, and was not designed as a human interface to easily create ad hoc queries and explore user data. In order to solve this problem, we provided a SQL engine with Open Distro for Elasticsearch, which we have been expanding since the initial release. As part of this continued investment, we are happy to announce new capabilities we are adding including a Kibana-based SQL Workbench and a new SQL CLI that will make it easier than ever for Open Distro for Elasticsearch users to use the SQL engine to work with their data.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is not only the de facto standard for data and analytics, but also one of the most popular languages among engineers and DevOps experts. Introducing SQL in Open Distro for Elasticsearch, allows users to manifest search results in a tabular format with documents represented as rows, fields represented as columns, and index names represented as a table names in the WHERE clause. This acts as a straightforward and declarative way to represent complex DSL queries in a readable format. The newly added tools, the SQL Workbench and the SQL CLI, in addition to the existing ODBC and JDBC drivers, and the SQL engine’s support for joins, and mathematical and string functions, can act as a powerful yet simplified way to extract and analyze data, and support complex analytics use cases.
Below is an overview of the features of the SQL engine in Open Distro for Elasticsearch.
Query Tools
- SQL Workbench A comprehensive and integrated visual tool to run on-demand SQL queries, translate SQL into its REST equivalent, and view and save results as text, JSON, JDBC or CSV

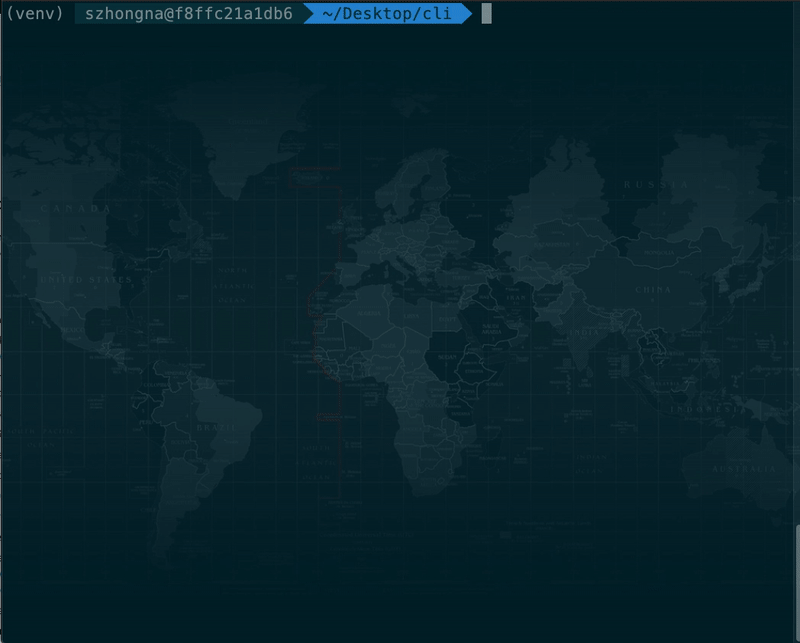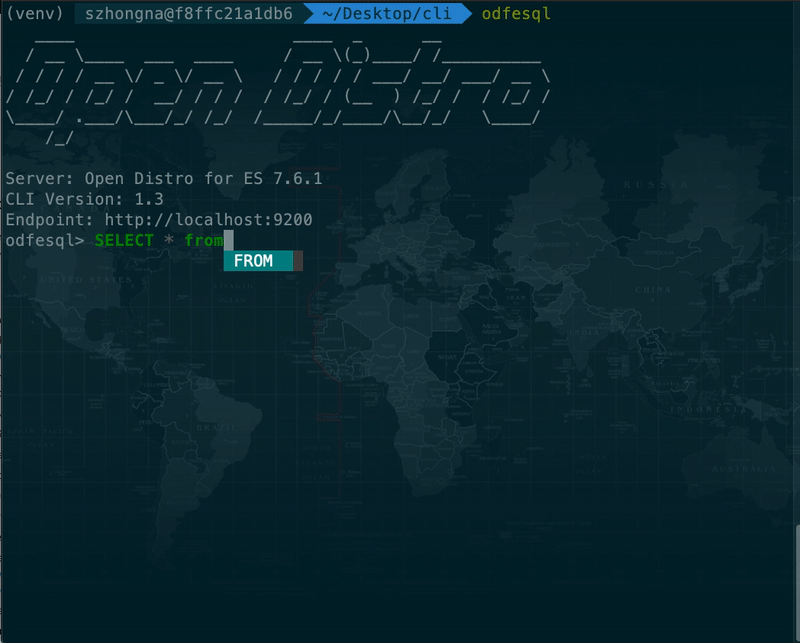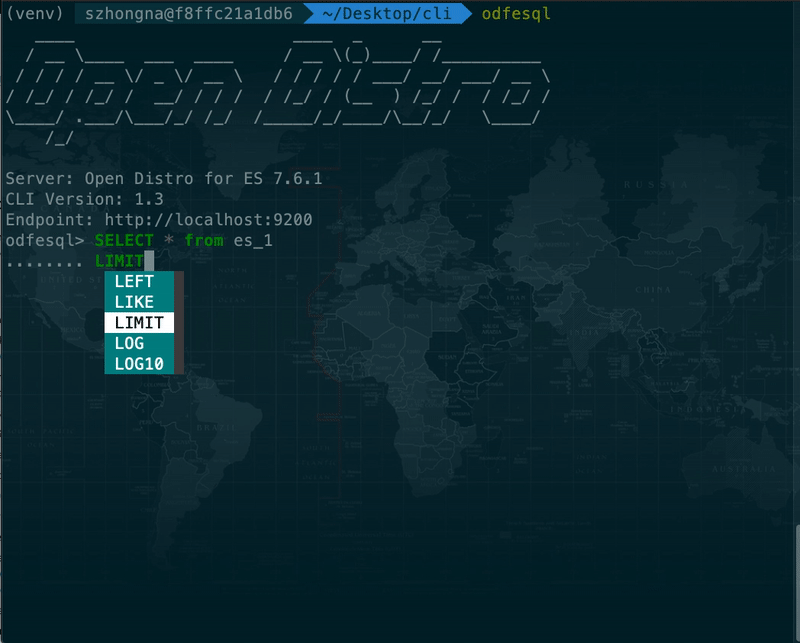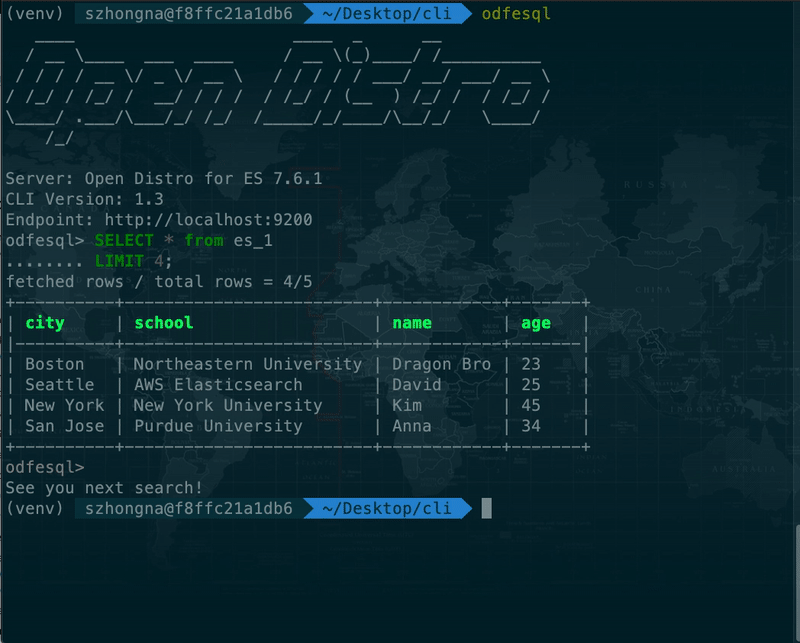
- SQL CLI An interactive stand-alone command line tool to run on-demand SQL queries, translate SQL into its REST equivalent, and view and save results as text, JSON, JDBC or CSV
Connectors and Drivers
- ODBC Driver Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) driver enables connecting with business intelligence (BI) applications such as Tableau, and exporting data to CSV and JSON
- JDBC Driver Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) driver enables connecting with business intelligence (BI) applications such as Tableau, and exporting data to CSV and JSON
Queries, Delete Support
- Basic Queries Support for SELECT clause, along with FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY, and LIMIT to search and aggregate data
- Complex Queries Support for complex queries such as subquery, join, union, and minus operating on more than one Elasticsearch index
- Metadata Queries Support for querying basic metadata about Elasticsearch indices using SHOW and DESCRIBE commands
- Delete Allows deleting of all the documents or documents that satisfy predicates in the WHERE clause from search results and not from the actual Elasticsearch index
JSON and Full-text search Support
- JSON Support for JSON by following PartiQL specification, a SQL-compatible query language that lets you query semi-structured and nested data for any data format
- Full-Text Search Support Support for full-text search on millions of documents using SQL commands
Functions and Operator Support
- Functions and Operators Support for string functions and operators, numeric functions and operators, and date-time functions by enabling field data in the document mapping
Settings
- Settings Allows viewing, configuring and modifying setting to control the behavior of SQL without need to restart/bounce the Elasticsearch cluster
Interfaces
- End points Explain shows the translated SQL query as Elasticsearch Query DSL, and cursor helps obtain a paginated response
Monitoring
- Monitoring Node level statistics can be obtained using stats endpoint
Request and Response Protocols
- Request Protocol Support for HTTP POST as a request protocol
- Response Protocols Support for response protocols such as JDBC, CSV, Elastic DSL, Raw Format
SQL engine in Open Distro for Elasticsearch provides a comprehensive, flexible and user friendly set of features to obtain search results from Elasticsearch in a declarative manner using SQL. To learn more, click here.
Have feedback on the SQL engine for Open Distro for Elasticsearch or any of the new tools? Suggestions, ideas and inputs from the OpenDistro for Elasticsearch community are always welcome. You can post your suggestions here.