How to start contributing to OpenSearch: A beginner’s guide based on my journey
OpenSearch is a powerful open-source search and analytics engine that empowers developers and organizations to build scalable, real-time search solutions. Whether you’re a student, developer, or open-source enthusiast, contributing to OpenSearch can significantly enhance your skills and reputation.
In this blog post I will walk you through:
- An introduction to OpenSearch.
- The benefits of contributing.
- Key areas you can contribute to.
- A step-by-step guide to your first code contribution.
- My personal tips for success.
Let’s get started!
What is OpenSearch?
OpenSearch is an open-source, distributed search and analytics engine. It was created as a fork of Elasticsearch in 2021 and is based on the Apache Lucene library. The project is hosted by the OpenSearch Software Foundation, under the Linux Foundation.
With over 130 GitHub repositories, OpenSearch has components and plugins built in a variety of programming languages like Java, Python, Kotlin, TypeScript, and JavaScript. This variety means there’s a space for everyone—whether you’re a front-end developer, a machine learning (ML) engineer, or someone interested in back-end systems.
Why should you contribute to OpenSearch?
1. Learn and grow
Contributing gives you hands-on experience with real-world projects. Unlike dummy projects, here you’re solving actual problems faced by the community.
2. Work on the tech you love
Sometimes, your day job may not involve your favorite tech stack. Open-source projects like OpenSearch can be your playground for exploring and building in the areas you’re passionate about. In my case, a strong interest in AI/ML motivated me to contribute to the OpenSearch ML Commons plugin.
3. Build your reputation
Every contribution—big or small—adds to your public portfolio. It can boost your career prospects and establish your presence in the open-source community.
4. Make an impact
Your code, reviews, or documentation could be used by thousands of community members across the world. You’re improving a project that powers mission-critical systems.
Areas of contribution to OpenSearch
You don’t need to be a coding wizard to make meaningful contributions to OpenSearch. The project offers a variety of ways to get involved, no matter your background or skill level.
- Code contributions are the most direct way to help. You can start by fixing bugs, adding small enhancements, or refactoring existing code. As you grow more confident, you might take on larger features or performance improvements.
- Bug reporting is crucial. If you use OpenSearch and encounter a problem, reporting it on GitHub with detailed steps, logs, and screenshots helps developers identify and resolve issues faster.
- Issue triage allows you to assist maintainers by verifying bugs, improving issue descriptions, or suggesting possible solutions.
- Code reviews not only improve the overall quality of contributions but also deepen your understanding of the codebase and project standards.
- Testing features during development or pre-release stages provides valuable user feedback that shapes the final product.
- Documentation work is highly valued—whether it’s updating existing docs, writing tutorials, or clarifying installation steps.
- Blogging or vlogging about your experience, solutions, and use cases helps build awareness and encourages others to contribute.
OpenSearch Project GitHub overview
Visit the OpenSearch Project on GitHub. You’ll find over 130 repositories related to:
- OpenSearch Core – The search engine itself (Java based).
- OpenSearch Dashboards – The UI for managing the engine (JavaScript/TypeScript).
- Plugins – ML, security, observability, etc.
- Utilities – Common utils, OpenSearch, Python clients, etc.
Choose the repo based on your interests and programming skills. I started with OpenSearch Core, then explored ML Commons to dive into the ML space.
Step by step: How to make your first contribution
Step 1: Set up GitHub and choose a repository
- Create a public GitHub account if you don’t have one.
- Fork the repository you want to contribute to (for example, https://github.com/opensearch-project/OpenSearch).
- Clone it to your local machine.
- Review these important files in the repo:
- README.md, CONTRIBUTING.md, CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- DEVELOPER_GUIDE.md
*Make sure your contribution aligns with the guidelines and is not restricted by your organization.
Step 2: Set up your development environment
Follow the developer guide (DEVELOPER_GUIDE.md) for the specific repo. For OpenSearch Core, you’ll typically need the following:
- JDK
- Gradle
- Docker (for integration tests)
- An IDE like IntelliJ or Eclipse
First, build and run tests without making any code changes. Once successful, try making small changes—like adding a log—to confirm that everything is set up.
Step 3: Find a “good first issue”
Search for issues labeled “good first issue” on the GitHub Issues tab. These are curated to help new contributors onboard easily. Before you start working on any issue, make sure no one else is already working on it by checking the assignee and reading the comments.
Tips for success: What I learned from my journey
Choosing the right “good first issue” can be overwhelming, but focusing on a few practical strategies made my journey smoother and more rewarding. Here are some key lessons that helped me succeed and can help others who are new to the ecosystem.
Start with test bugs
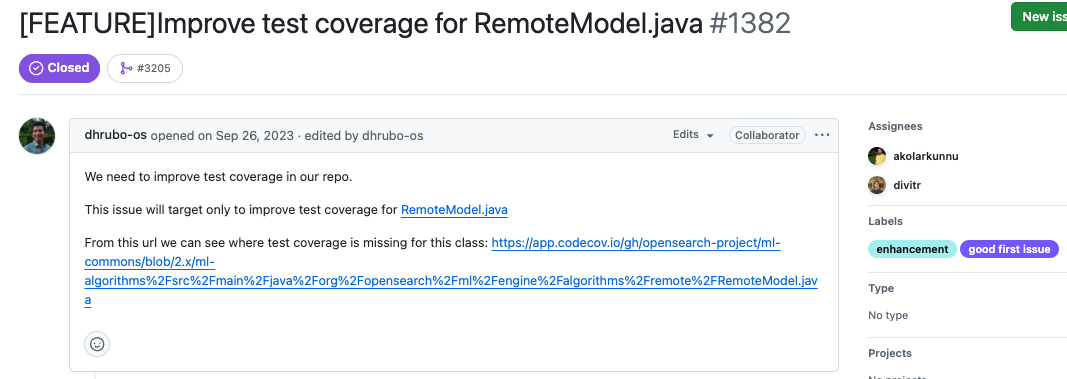
When beginning my OpenSearch journey, I intentionally looked for test bugs to contribute to. These are typically self-contained, low-risk issues that don’t involve changes to complex business logic. That makes them less intimidating and perfect for understanding how a project is structured. For instance, my first contributions were to OpenSearch Core and ML Commons, where I worked on fixing test issues or improving test coverage. These types of bugs are also reviewed faster, which provides early feedback that is crucial when you’re still learning the project’s workflow and coding standards. Fixing test bugs gave me confidence and helped me build familiarity with the repositories.
GitHub reference: https://github.com/opensearch-project/ml-commons/issues/1382
Work in your area of expertise
Playing to your strengths is a great way to make meaningful contributions early on. I have a background in OpenJDK, so I looked for issues that aligned with my experience— particularly those related to locale handling and internationalization. One such task involved replacing deprecated locale provider Compat with Common Locale Data Repository (CLDR). Leveraging what you already know reduces your ramp-up time and increases your impact.
GitHub reference: https://github.com/opensearch-project/OpenSearch/issues/11550
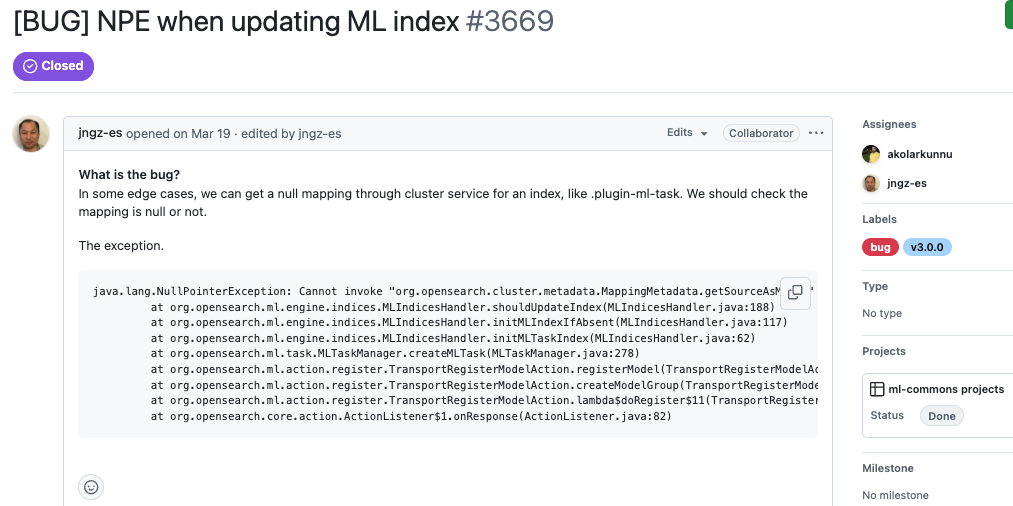
Choose issues with stack traces
When a GitHub issue includes a stack trace, it serves as a roadmap to the problem. It tells you exactly where the failure occurred—often down to the class and method. I found that these types of issues were much easier to debug because I could jump straight into the relevant part of the codebase. It eliminates a lot of guesswork and lets you focus on reproducing and fixing the bug. This is especially helpful in large projects where navigating the codebase can otherwise be daunting.
GitHub reference: https://github.com/opensearch-project/ml-commons/issues/3669
Look for well-described issues
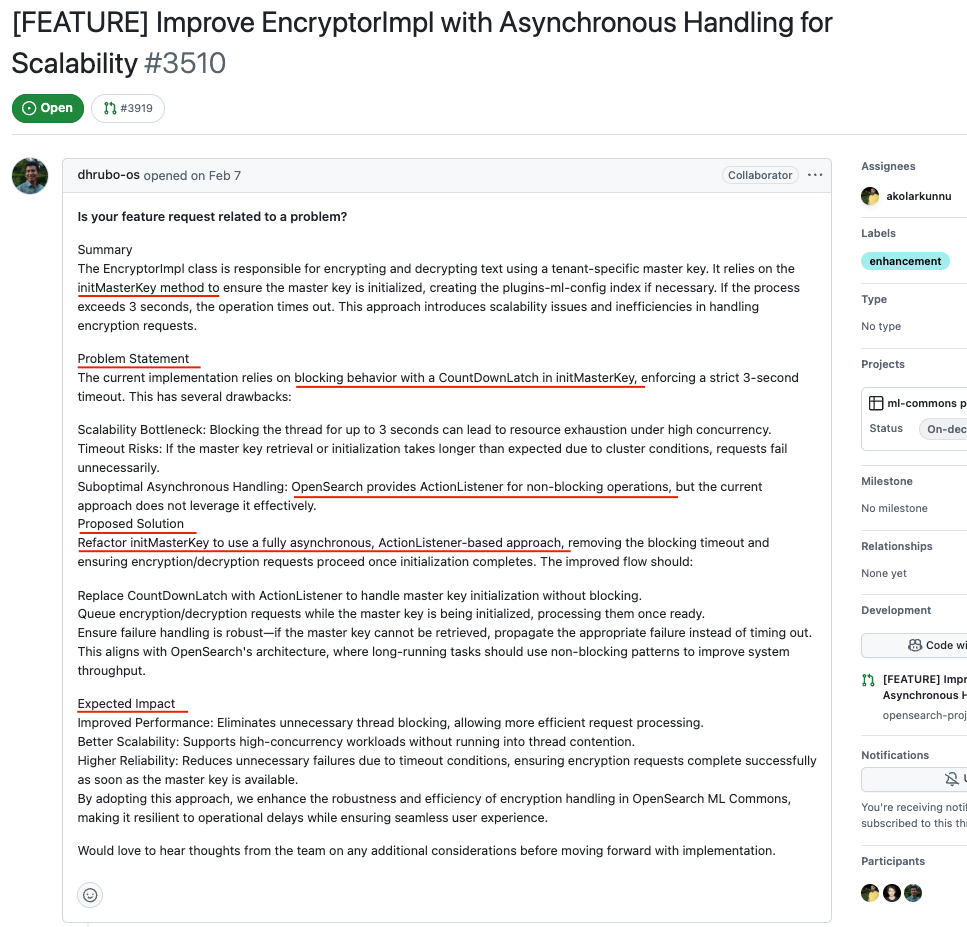
Some maintainers go above and beyond when writing bug reports or feature requests. They not only explain the issue but also provide helpful context, potential solutions, and notes on what parts of the code are affected. As a beginner, these are pure gold. They act as mini-tutorials and can drastically reduce the time it takes to understand and fix the problem.
One memorable example was a performance issue tied to a method called initMasterKey() of EncryptorImpl. The report clearly identified the use of CountDownLatch as the bottleneck and suggested replacing it with an ActionListener. With such guidance, making the fix felt much more approachable and satisfying.
GitHub reference: https://github.com/opensearch-project/ml-commons/issues/3510
*Pro tip: Focus on learning the contribution process through your first few pull requests (PRs) rather than trying to solve complex bugs.
After finalizing the issue you’re working on, leave a comment to assign it to yourself—this helps prevent others from unknowingly working on the same issue.
Step 4: Make the fix and create a PR
- Create a new branch from main.
- Make your changes and commit them.
- Push your branch and create a PR.
- Follow the repo’s PR template and wait for CI checks.
- Respond to review comments and revise your PR as needed.
Engaging with the community
Slack
One of the best ways to get involved is by joining the OpenSearch community on Slack. Each major component—like Dashboards, Search, or ML—has its own dedicated channel. These spaces are great for asking questions, discussing implementation details, or sharing your progress. Don’t be afraid to reach out. The maintainers and other contributors are generally very welcoming and helpful, especially to new contributors. Being active in these channels not only speeds up your learning curve but also helps you stay updated on ongoing developments.
Slack link: https://opensearch.org/slack.html
Triage meetings
OpenSearch holds regular triage meetings where maintainers review and prioritize issues. Attending these meetings is a great way to get visibility into what is important to the project. It’s also the perfect time to introduce yourself, express your interest, and ask for guidance on where to start. Maintainers often suggest beginner-friendly issues during these meetings, making it easier to find one aligned with your skills.
Meeting invite link: https://www.meetup.com/opensearch/events/
YouTube
The OpenSearch YouTube channel is filled with useful content, including tutorials, demos, and community talks. These videos offer deep insights into how different components work and how people are using or contributing to them. Watching these helped me understand the ecosystem better.
YouTube channel link: https://www.youtube.com/@OpenSearchProject
Meetups and conferences
Participating in local OpenSearch community meetups or OpenSearchCon events is another great way to connect with contributors and maintainers. These in-person events foster real-time collaboration, help you build your network, and deepen your engagement with the project.
Find your nearby user group here: https://opensearch.org/user-groups/.
Final step: Submit and stay engaged
After submitting your first PR:
- Watch your repositories on GitHub.
- Review others’ PRs.
- Attend community events.
- Share what you learn in blog posts or event talks.
Your open-source journey has officially begun!
⸻
OpenSearch is not just a tool—it’s a community. Whether you fix a test bug or build a new feature, your contributions matter.
My advice:
Start small, grow steadily, and never hesitate to ask for help. Everyone in the community wants to see you succeed.