In the world of search and analytics, performance is everything. As an engineer, you need to ensure that your search queries are not only fast but also resource efficient. However, understanding what’s happening in your search operations internally can be challenging. That’s where OpenSearch’s new feature, Query Insights, comes into play. This tool is designed to give you deeper visibility into the performance of your search queries, helping you identify bottlenecks, optimize performance, and, ultimately, provide a better experience for your users.
What is Query Insights?
Query Insights is a comprehensive framework within OpenSearch that provides detailed visibility into the execution of search queries. It collects and analyzes data on the performance of each query, offering you the tools to identify the top resource-consuming queries, understand query latency, and track the source of queries. This feature is invaluable for troubleshooting, optimizing performance, and ensuring the smooth operation of your search environment.
Why is Query Insights important?
Understanding the performance of your search queries is critical for maintaining a responsive and efficient search platform. With Query Insights, you can quickly identify the top queries that are consuming the most CPU or memory or are exhibiting high latency. This allows you to focus your optimization efforts where they are needed most. By using Query Insights, you can:
- Identify performance bottlenecks: Easily spot queries that are slowing down your system, whether due to high resource usage or inefficient execution.
- Optimize resource allocation: Gain insights into how resources are being utilized, enabling you to make informed decisions about shard rebalancing or scaling.
- Enhance troubleshooting: With detailed metadata and query execution stages, you can drill down into specific nodes or tasks to pinpoint the root cause of performance issues.
Key features of Query Insights
- Top N queries: One of the most requested features is the ability to identify the top queries by latency, CPU usage, or memory consumption. This feature allows you to focus on optimizing the queries that have the most significant impact on your system’s performance.
- Detailed query metadata: Each query record includes essential information such as the timestamp, source, involved indexes, node ID, and task-level resource usage. This data is crucial for understanding the context of each query and making informed decisions about optimizations.
- Query exporter: The Query Insights framework includes an exporter that allows you to save query performance data to local indexes or a data lake. This historical data can be invaluable for investigating past performance issues, such as CPU spikes or node drops.
- Upcoming dashboard integration: An upcoming feature is the Query Insights dashboard, which will offer a visual representation of the top queries and their performance metrics. This dashboard will make it even easier to monitor and analyze query performance over time.
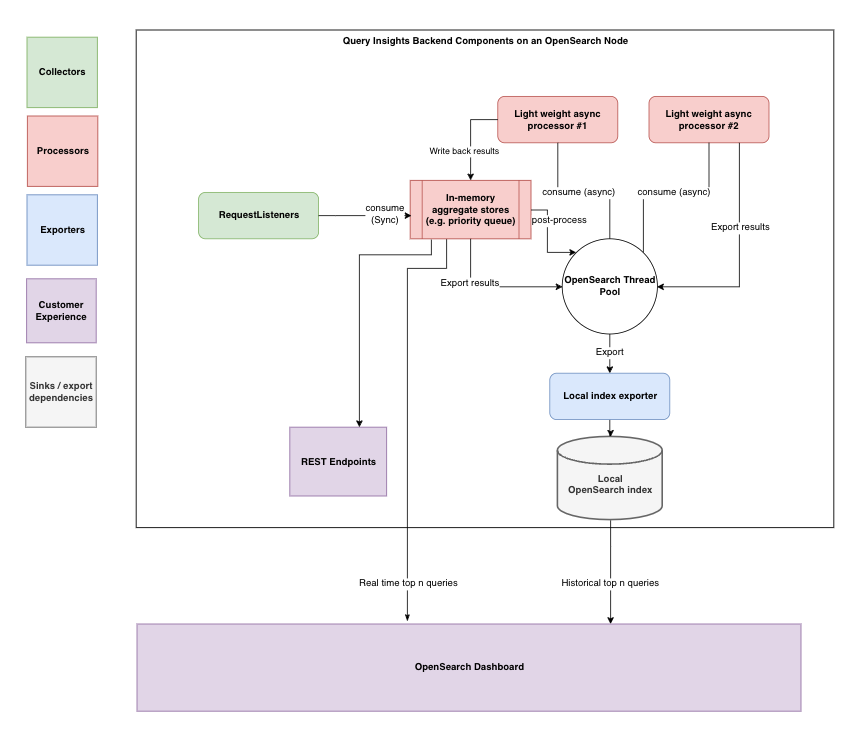
Architecture
The Query Insights architecture includes the new Query Insights plugin, additional OpenSearch components, and the integration of existing components to collect metrics, delivering comprehensive insights and recommendations. At a high level, the Query Insights framework comprises the following integral components:
- Collectors: These components gather performance-related data at various stages of search query execution.
- Processors: Built into the Query Insights plugin, these components perform lightweight aggregation and processing on data gathered by the collectors.
- Customer experience: Various user interaction points, such as APIs, dashboards, metrics, and exporters, facilitate the presentation of insights and recommendations to users.
The interactions among these components are shown in the following architecture diagram.
Examples
To better illustrate the power of Query Insights, let’s explore some practical use cases and see how this tool can streamline your search optimization efforts.
Example 1: Identify resource-intensive queries (top N queries by CPU usage)
Scenario: You notice that your OpenSearch cluster is experiencing high CPU usage. To investigate, you want to track the top N queries by CPU usage within a 30-minute window.
Steps:
- Enable top N query monitoring by CPU:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.cpu.enabled" : true } } - Set the monitoring window size to 30 minutes:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.cpu.window_size" : "30m" } } - Set N to 10 to track the top 10 queries:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.cpu.top_n_size" : 10 } } - Retrieve the top N queries by CPU:
GET /_insights/top_queries?type=cpu
The response returns the 10 queries that used the most CPU resources within the last 30 minutes, helping you identify which queries to optimize.
Example 2: Diagnose slow search queries (top N queries by latency)
Scenario: Your users are reporting slow search queries, and you need to find the most time-consuming queries executed in the last hour.
Steps:
- Enable top N query monitoring by latency:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.latency.enabled" : true } } - Set the monitoring window size to 1 hour:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.latency.window_size" : "60m" } } - Set N to track the top 5 queries by latency:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.latency.top_n_size" : 5 } } - Retrieve the top N queries by latency:
GET /_insights/top_queries?type=latency
The response provides a list of the five slowest queries executed in the last hour, allowing you to investigate further.
Example 3: Group similar queries for better analysis (top N queries by similarity)
Scenario: A single query is executed multiple times with small variations, preventing other resource-heavy queries from appearing in the top N query list. You want to group similar queries based on their structure.
Steps:
- Enable top N query monitoring by CPU or latency:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.cpu.enabled" : true } } - Enable query grouping by similarity:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.group_by" : "similarity" } } - Optionally, limit the number of monitored query groups:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.max_groups_excluding_topn" : 100 } } - Retrieve the top N query groups:
GET /_insights/top_queries
By grouping similar queries, you ensure that the results contain a greater variety of queries, making it easier to identify other resource-intensive queries.
Example 4: Export Query Insights data for offline analysis
Scenario: You want to export top N query data to local indexes for offline analysis.
Steps:
- Enable top N query monitoring (for example, by latency):
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.latency.enabled" : true } } - Configure a local index exporter:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "search.insights.top_queries.latency.exporter.type" : "local_index", "search.insights.top_queries.latency.exporter.config.index" : "top_queries-YYYY.MM.dd" } }
This request will store daily top N query data in your local index, allowing for extended historical analysis.
How Query Insights can benefit you
Whether you’re running a small cluster or managing a large-scale search platform, Query Insights can help you maintain optimal performance. By leveraging the detailed insights provided by this tool, you can:
- Proactively manage performance: With real-time visibility into query execution, you can identify and address potential performance issues before they impact your users.
- Make data-driven decisions: Use the detailed metrics provided by Query Insights to inform decisions about scaling, resource allocation, and performance tuning.
- Improve user experience: By optimizing the performance of your search queries, you ensure that your users get fast, relevant search results every time.
Conclusion
Query Insights is a useful tool for anyone responsible for maintaining the performance and reliability of an OpenSearch environment. Using Query Insights, you can gain a deeper understanding of how your search queries are performing and take actions to optimize them. Whether you’re troubleshooting a specific issue or looking to improve overall system efficiency, Query Insights provides the tools you need to succeed. Keep an eye out for the upcoming dashboard feature, which will further enhance your ability to monitor and analyze your search queries in real time.
To learn more about Query Insights, check out the documentation.