We’re thrilled to announce the launch of OpenSearch AI demos in Hugging Face, a set of cutting-edge demo applications that put the power of advanced AI search capabilities right at your fingertips. Whether you’re a machine learning (ML) engineer, search expert, data wizard, or product owner diving into the world of generative AI, OpenSearch AI demos are part of your new go-to playground for exploring and understanding the latest in search technology.
OpenSearch AI Search is a comprehensive demo platform that showcases the full spectrum of AI search capabilities using OpenSearch. It includes three main modules:
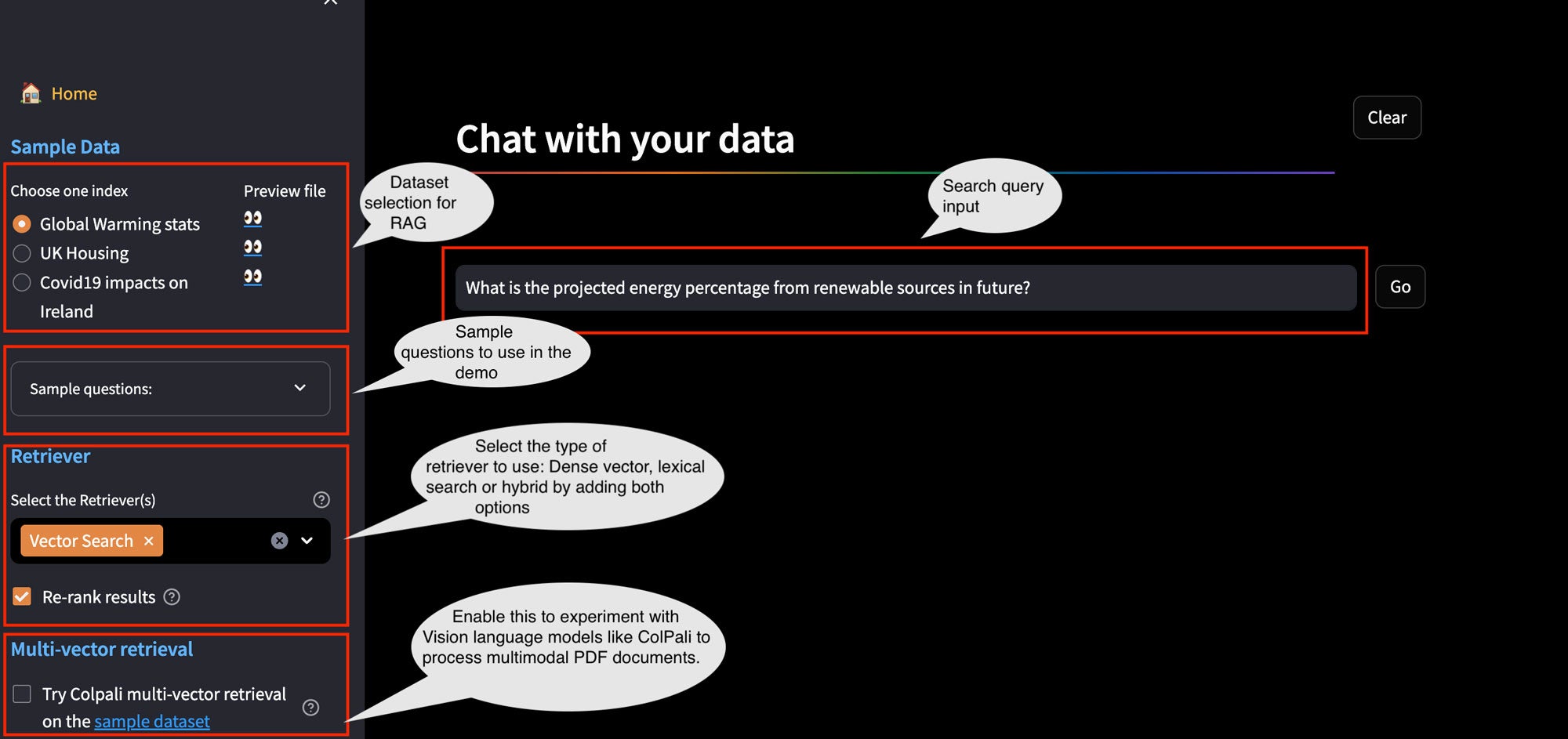
- AI Search: Demonstrates AI search capabilities with OpenSearch (lexical search, neural sparse search, dense vector search, hybrid search, multimodal search). The AI Search module also demonstrates using large language models (LLMs) to improve search. The solution uses LLMs in two key ways: to rewrite queries with metadata filters for better retrieval, and to judge relevance, helping compare the impact of different search types on quality. Additionally, this section covers tuning hybrid search weightage per subquery and demonstrates how reranking helps improve the relevance of your search. In this demo, we use a dataset that contains 2,465 retail product samples that belong to different categories such as accessories, home decor, apparel, housewares, books, and instruments. Each product contains metadata, including the ID, current stock, name, category, style, description, price, image URL, and gender affinity of the product. The following image shows the AI Search UI.
- Multimodal RAG: Using multimodal retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), you can unlock the insights hidden within unstructured PDF documents. Many PDFs contain multimodal elements like text, tables, and images, and relying solely on text-based processing risks overlooking critical information. This section addresses this challenge using two approaches:
- Grounding multi-modalities to text: Sample PDFs are parsed using multimodal parsers like the Unstructured Python module, where images and tables are summarized into text and stored as both sparse and dense vectors. Metadata links each chunk to its source (text, image, or table), enabling retrieval for question answering.
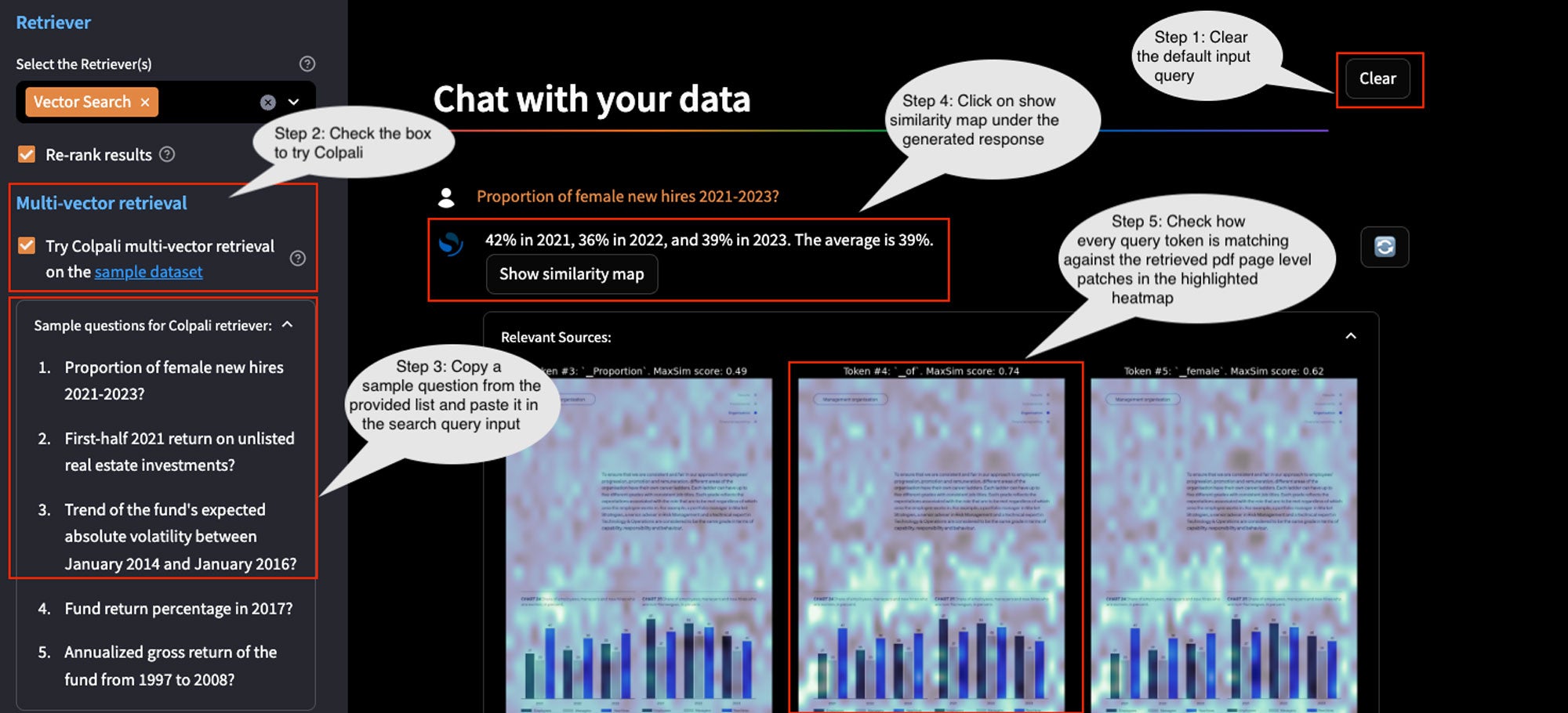
- Using cutting-edge vision-language models for information retrieval: Multi-vector late interaction models like ColPaLi avoid the need for complex pipelines to process multimodal PDFs by generating multiple page-level vectors that capture all modalities. These localized representations enable fine-grained interactions between query tokens and image patches of PDF pages, allowing ColPaLi to compute high-resolution relevance scores across spatial layouts. A key advantage is interpretability: similarity scores can be visualized as heat maps over PDF pages, highlighting which segments—such as text blocks, tables, or figure captions—contributed most to retrieval (depicted in the following image). This solution uses a dataset consisting of images of 6,692 PDF pages (with text, tables, and charts) of public reports retrieved from Norwegian Government Pension Fund Global.
- AI shopping assistant: While RAG is widely known for building QA systems over unstructured data, its application in e-commerce product search opens new possibilities for transforming the user experience. In this solution, we explore how combining RAG with AI agents on top of your OpenSearch product catalog creates an agentic shopping assistant capable of delivering a conversational shopping experience. By equipping the agent with capabilities such as user intent understanding, query rewriting, dynamic selection of search strategies, search result evaluation, feedback-based retries, and personalization, we enable adaptive, high-quality retrieval over product catalogs. This approach not only improves relevance but also allows users to interact naturally with the search system. In this module, we use a dataset derived from the original Amazon ESCI e-commerce dataset. We use a subset of items under the “apparel” and “footwear” product categories with a total of 59.3K products. A sample AI shopping assistant interaction is depicted in the following image.
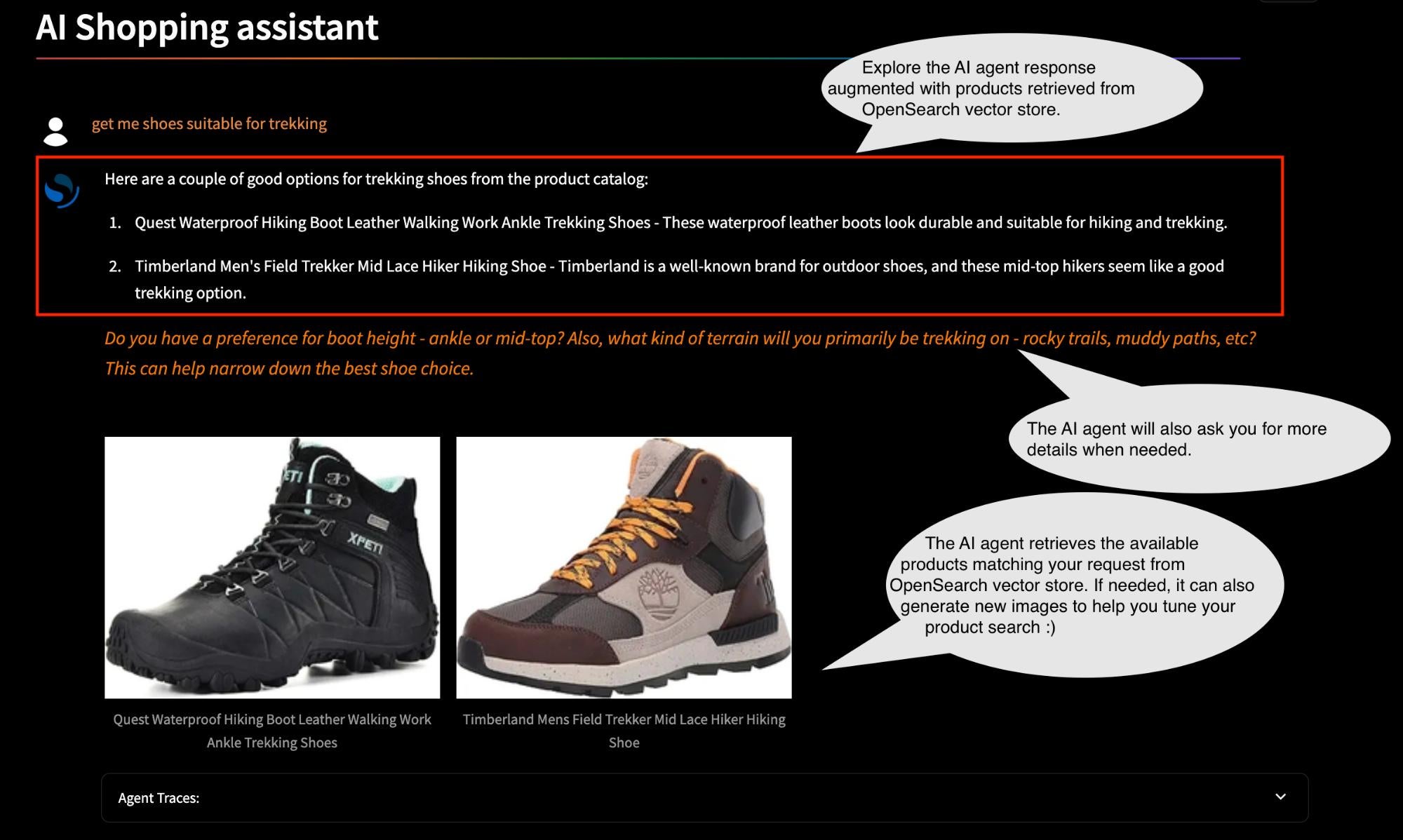
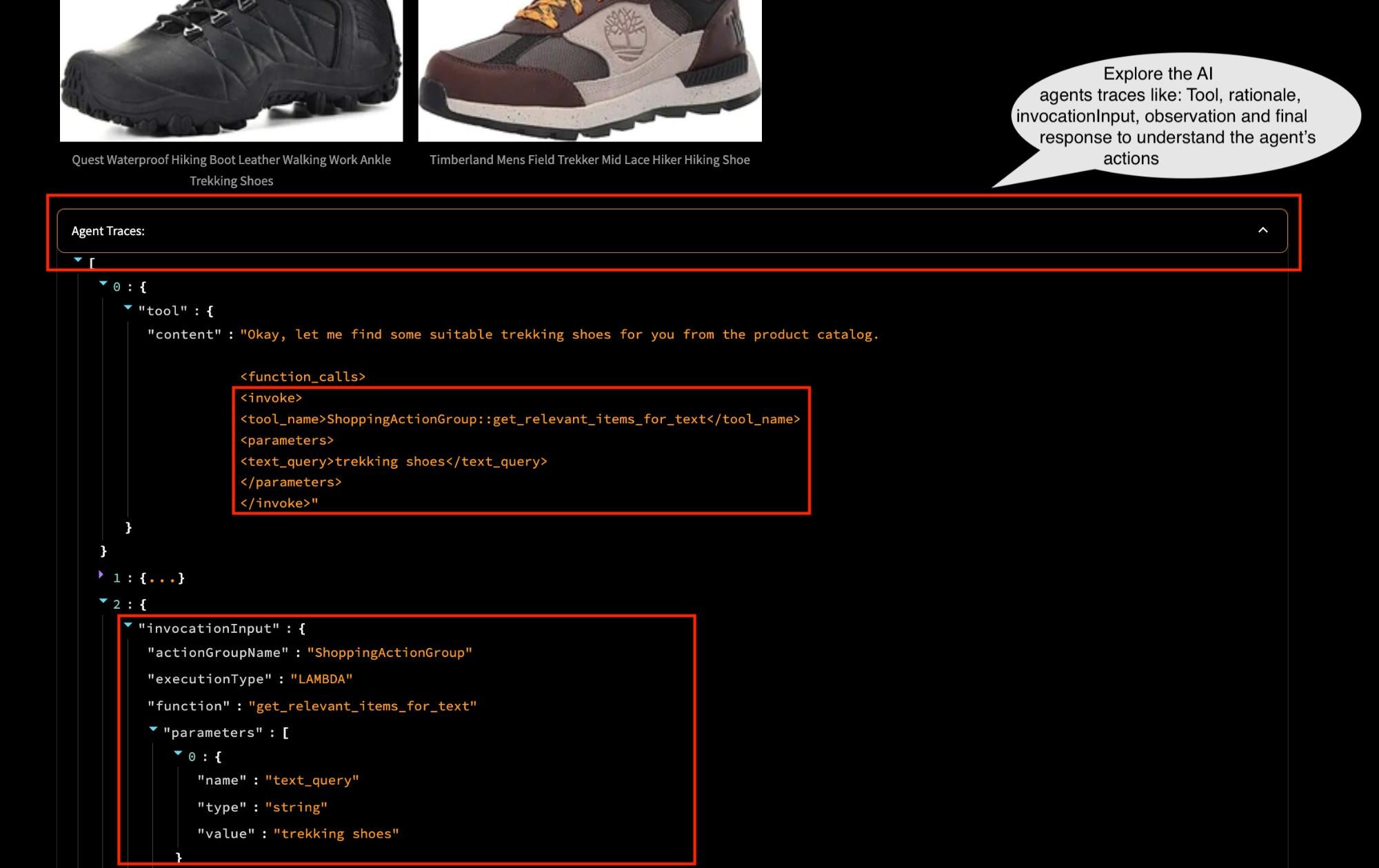
The AI agent in this demo has the following defined tools:
get_relevant_items_for_image: Retrieves relevant products based on the provided image and text query by running a multimodal search.generate_image: Generates images based on the provided text description.get_product_details: Retrieves details about a specific product by looking up the OpenSearch index.get_relevant_items_for_text: Retrieves relevant products based on the provided text query by running a semantic search.get_any_general_recommendation: Provides fashion recommendations related to a specific product or in general.retrieve_with_keyword_search: Retrieves relevant products based on the provided text query by running a lexical search.
Under the hood: OpenSearch AI search demo architecture
ML integration in search systems significantly enhances user experience throughout the entire lifecycle, from ingesting documents to delivering highly relevant results. OpenSearch facilitates this integration through a list of supported ML connectors, enabling seamless interaction with ML and LLMs deployed on ML platforms such as Amazon SageMaker AI and Amazon Bedrock. The following image presents the AI search demo architecture.
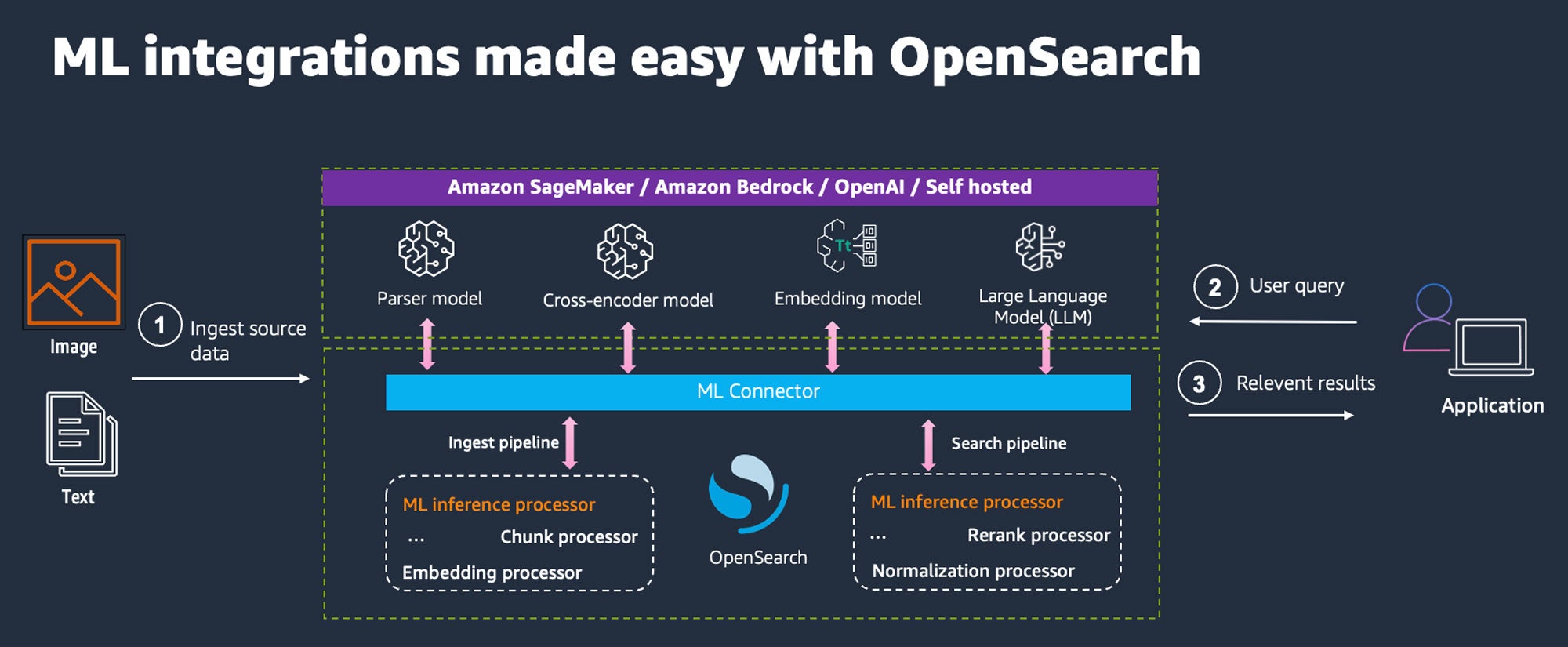
OpenSearch supports dual-pipeline architecture—comprising ingest and search pipelines—providing a robust framework for ML-driven search optimization.
During ingestion, documents undergo ML-powered processing, using a combination of ingest processors within the ingest pipeline to chunk long text documents and generate text embeddings. During search, search pipelines use the power of search processors to transform queries, normalize hybrid search scores, and apply LLMs for text generation.
OpenSearch ML integrations enable advanced search functionalities such as hybrid search, query rewriting, and RAG, effectively bridging the gap between traditional information retrieval and state-of-the-art ML techniques.
Key benefits
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI and search technologies, it’s crucial to understand which approaches work best for different use cases. OpenSearch AI demos allow you to perform the following tasks:
- Compare and contrast search types: Test different AI search types side by side to see how they perform for your specific needs.
- Explore cutting-edge techniques: Get hands-on experience with state-of-the-art methods like query rewriting using LLMs and multi-vector search with ColPali in RAG.
- Witness agents in action: See how intelligent agents can enhance the search experience in real time.
- One-stop shop: Access all these advanced search techniques integrated with ML and LLMs in a single user-friendly platform.
Start exploring
OpenSearch AI demos are built for practical experimentation and learning. Here’s how to get started:
- Go to the OpenSearch AI demos application and start experimenting with different AI search use cases.
- Try various queries for your use case, compare results, and see which techniques work best.
- Got ideas for improvements? Check out our GitHub repo to request features, report bugs, or contribute to OpenSearch AI demos.
- Are you an AWS builder? Check out this hands-on experience to build a next-generation search demo in your own AWS account.
Ready to revolutionize your approach to AI search? Dive into OpenSearch AI demos today and discover the future of search technology!
