You're viewing version 2.16 of the OpenSearch documentation. This version is no longer maintained. For the latest version, see the current documentation. For information about OpenSearch version maintenance, see Release Schedule and Maintenance Policy.
Complex queries
Besides simple SFW (SELECT-FROM-WHERE) queries, the SQL plugin supports complex queries such as subquery, join, union, and minus. These queries operate on more than one OpenSearch index. To examine how these queries execute behind the scenes, use the explain operation.
Joins
OpenSearch SQL supports inner joins, cross joins, and left outer joins.
Constraints
Joins have a number of constraints:
- You can only join two indexes.
- You must use aliases for indexes (for example,
people p). - Within an ON clause, you can only use AND conditions.
-
In a WHERE statement, don’t combine trees that contain multiple indexes. For example, the following statement works:
WHERE (a.type1 > 3 OR a.type1 < 0) AND (b.type2 > 4 OR b.type2 < -1)The following statement does not:
WHERE (a.type1 > 3 OR b.type2 < 0) AND (a.type1 > 4 OR b.type2 < -1) - You can’t use GROUP BY or ORDER BY for results.
- LIMIT with OFFSET (e.g.
LIMIT 25 OFFSET 25) is not supported.
Description
The JOIN clause combines columns from one or more indexes using values common to each.
Syntax
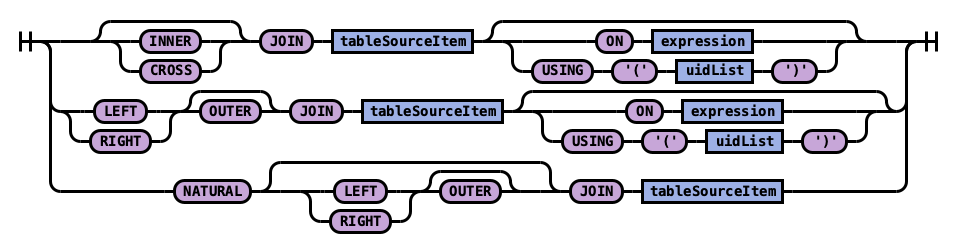
Rule tableSource:

Rule joinPart:
Example 1: Inner join
Inner join creates a new result set by combining columns of two indexes based on your join predicates. It iterates the two indexes and compares each document to find the ones that satisfy the join predicates. You can optionally precede the JOIN clause with an INNER keyword.
The join predicate(s) is specified by the ON clause.
SQL query:
SELECT
a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname,
e.id, e.name
FROM accounts a
JOIN employees_nested e
ON a.account_number = e.id
Explain:
The explain output is complicated, because a JOIN clause is associated with two OpenSearch DSL queries that execute in separate query planner frameworks. You can interpret it by examining the Physical Plan and Logical Plan objects.
{
"Physical Plan" : {
"Project [ columns=[a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname, e.name, e.id] ]" : {
"Top [ count=200 ]" : {
"BlockHashJoin[ conditions=( a.account_number = e.id ), type=JOIN, blockSize=[FixedBlockSize with size=10000] ]" : {
"Scroll [ employees_nested as e, pageSize=10000 ]" : {
"request" : {
"size" : 200,
"from" : 0,
"_source" : {
"excludes" : [ ],
"includes" : [
"id",
"name"
]
}
}
},
"Scroll [ accounts as a, pageSize=10000 ]" : {
"request" : {
"size" : 200,
"from" : 0,
"_source" : {
"excludes" : [ ],
"includes" : [
"account_number",
"firstname",
"lastname"
]
}
}
},
"useTermsFilterOptimization" : false
}
}
}
},
"description" : "Hash Join algorithm builds hash table based on result of first query, and then probes hash table to find matched rows for each row returned by second query",
"Logical Plan" : {
"Project [ columns=[a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname, e.name, e.id] ]" : {
"Top [ count=200 ]" : {
"Join [ conditions=( a.account_number = e.id ) type=JOIN ]" : {
"Group" : [
{
"Project [ columns=[a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname] ]" : {
"TableScan" : {
"tableAlias" : "a",
"tableName" : "accounts"
}
}
},
{
"Project [ columns=[e.name, e.id] ]" : {
"TableScan" : {
"tableAlias" : "e",
"tableName" : "employees_nested"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
Result set:
| a.account_number | a.firstname | a.lastname | e.id | e.name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Hattie | Bond | 6 | Jane Smith |
Example 2: Cross join
Cross join, also known as cartesian join, combines each document from the first index with each document from the second. The result set is the cartesian product of documents of both indexes. This operation is similar to the inner join without the ON clause that specifies the join condition.
It’s risky to perform cross join on two indexes of large or even medium size. It might trigger a circuit breaker that terminates the query to avoid running out of memory.
SQL query:
SELECT
a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname,
e.id, e.name
FROM accounts a
JOIN employees_nested e
Result set:
| a.account_number | a.firstname | a.lastname | e.id | e.name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amber | Duke | 3 | Bob Smith |
| 1 | Amber | Duke | 4 | Susan Smith |
| 1 | Amber | Duke | 6 | Jane Smith |
| 6 | Hattie | Bond | 3 | Bob Smith |
| 6 | Hattie | Bond | 4 | Susan Smith |
| 6 | Hattie | Bond | 6 | Jane Smith |
| 13 | Nanette | Bates | 3 | Bob Smith |
| 13 | Nanette | Bates | 4 | Susan Smith |
| 13 | Nanette | Bates | 6 | Jane Smith |
| 18 | Dale | Adams | 3 | Bob Smith |
| 18 | Dale | Adams | 4 | Susan Smith |
| 18 | Dale | Adams | 6 | Jane Smith |
Example 3: Left outer join
Use left outer join to retain rows from the first index if it does not satisfy the join predicate. The keyword OUTER is optional.
SQL query:
SELECT
a.account_number, a.firstname, a.lastname,
e.id, e.name
FROM accounts a
LEFT JOIN employees_nested e
ON a.account_number = e.id
Result set:
| a.account_number | a.firstname | a.lastname | e.id | e.name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amber | Duke | null | null |
| 6 | Hattie | Bond | 6 | Jane Smith |
| 13 | Nanette | Bates | null | null |
| 18 | Dale | Adams | null | null |
Subquery
A subquery is a complete SELECT statement used within another statement and enclosed in parenthesis. From the explain output, you can see that some subqueries are actually transformed to an equivalent join query to execute.
Example 1: Table subquery
SQL query:
SELECT a1.firstname, a1.lastname, a1.balance
FROM accounts a1
WHERE a1.account_number IN (
SELECT a2.account_number
FROM accounts a2
WHERE a2.balance > 10000
)
Explain:
{
"Physical Plan" : {
"Project [ columns=[a1.balance, a1.firstname, a1.lastname] ]" : {
"Top [ count=200 ]" : {
"BlockHashJoin[ conditions=( a1.account_number = a2.account_number ), type=JOIN, blockSize=[FixedBlockSize with size=10000] ]" : {
"Scroll [ accounts as a2, pageSize=10000 ]" : {
"request" : {
"size" : 200,
"query" : {
"bool" : {
"filter" : [
{
"bool" : {
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"must" : [
{
"bool" : {
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"must" : [
{
"bool" : {
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"must_not" : [
{
"bool" : {
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"must_not" : [
{
"exists" : {
"field" : "account_number",
"boost" : 1
}
}
],
"boost" : 1
}
}
],
"boost" : 1
}
},
{
"range" : {
"balance" : {
"include_lower" : false,
"include_upper" : true,
"from" : 10000,
"boost" : 1,
"to" : null
}
}
}
],
"boost" : 1
}
}
],
"boost" : 1
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1
}
},
"from" : 0
}
},
"Scroll [ accounts as a1, pageSize=10000 ]" : {
"request" : {
"size" : 200,
"from" : 0,
"_source" : {
"excludes" : [ ],
"includes" : [
"firstname",
"lastname",
"balance",
"account_number"
]
}
}
},
"useTermsFilterOptimization" : false
}
}
}
},
"description" : "Hash Join algorithm builds hash table based on result of first query, and then probes hash table to find matched rows for each row returned by second query",
"Logical Plan" : {
"Project [ columns=[a1.balance, a1.firstname, a1.lastname] ]" : {
"Top [ count=200 ]" : {
"Join [ conditions=( a1.account_number = a2.account_number ) type=JOIN ]" : {
"Group" : [
{
"Project [ columns=[a1.balance, a1.firstname, a1.lastname, a1.account_number] ]" : {
"TableScan" : {
"tableAlias" : "a1",
"tableName" : "accounts"
}
}
},
{
"Project [ columns=[a2.account_number] ]" : {
"Filter [ conditions=[AND ( AND account_number ISN null, AND balance GT 10000 ) ] ]" : {
"TableScan" : {
"tableAlias" : "a2",
"tableName" : "accounts"
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
Result set:
| a1.firstname | a1.lastname | a1.balance |
|---|---|---|
| Amber | Duke | 39225 |
| Nanette | Bates | 32838 |
Example 2: From subquery
SQL query:
SELECT a.f, a.l, a.a
FROM (
SELECT firstname AS f, lastname AS l, age AS a
FROM accounts
WHERE age > 30
) AS a
Explain:
{
"from" : 0,
"size" : 200,
"query" : {
"bool" : {
"filter" : [
{
"bool" : {
"must" : [
{
"range" : {
"age" : {
"from" : 30,
"to" : null,
"include_lower" : false,
"include_upper" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
},
"_source" : {
"includes" : [
"firstname",
"lastname",
"age"
],
"excludes" : [ ]
}
}
Result set:
| f | l | a |
|---|---|---|
| Amber | Duke | 32 |
| Dale | Adams | 33 |
| Hattie | Bond | 36 |