Token graphs
Token graphs show how tokens relate to each other during text analysis, particularly when handling multi-word synonyms or compound words. They help ensure accurate query matching and phrase expansion.
Each token is assigned the following metadata:
-
position– The location of the token in the text -
positionLength– How many positions the token spans (used in multi-word expressions)
Token graphs use this information to build a graph structure of token relationships, which is later used during query parsing. Graph-aware token filters, such as synonym_graph and word_delimiter_graph, enable you to match phrases more accurately.
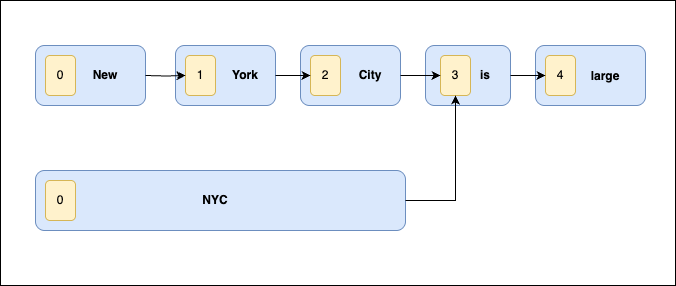
The following diagram depicts the relationship between position and positionLength when using synonym_graph. The “NYC” token is assigned a position of 0 and a positionLength of 3.
Using token graphs during indexing and querying
At index time, positionLength is ignored and token graphs are not used.
During query execution, various query types can leverage token graphs, with the following being the most frequently used:
Example: Synonym compared to synonym graph
To better understand the difference between graph-aware token filters and standard token filters, you can use the following steps to compare the synonym token filter with the synonym_graph token filter:
-
Create an index with a
synonymtoken filter (not graph aware):PUT /synonym_index { "settings": { "analysis": { "filter": { "my_synonyms": { "type": "synonym", "synonyms": ["ssd => solid state drive"] } }, "analyzer": { "my_analyzer": { "tokenizer": "standard", "filter": ["lowercase", "my_synonyms"] } } } }, "mappings": { "properties": { "content": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "my_analyzer" } } } } -
Create an index with a
synonym_graphtoken filter (graph aware):PUT /synonym_graph_index { "settings": { "analysis": { "filter": { "my_synonyms": { "type": "synonym_graph", "synonyms": ["ssd => solid state drive"] } }, "analyzer": { "my_analyzer": { "tokenizer": "standard", "filter": ["lowercase", "my_synonyms"] } } } }, "mappings": { "properties": { "content": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "my_analyzer" } } } } -
Create the same document in each index:
PUT /synonym_index/_doc/1 { "content": "ssd is critical" }PUT /synonym_graph_index/_doc/1 { "content": "ssd is critical" } -
Search the non-graph-aware index:
POST /synonym_index/_search { "query": { "match_phrase": { "content": "solid state drive is critical" } } }The response contains no hits:
{ "took": 13, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": { "value": 0, "relation": "eq" }, "max_score": null, "hits": [] } } -
Search the graph-aware index:
POST /synonym_graph_index/_search { "query": { "match_phrase": { "content": "solid state drive is critical" } } }The response contains one hit:
{ "took": 9, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": { "value": 1, "relation": "eq" }, "max_score": 1.4384103, "hits": [ { "_index": "synonym_graph_index", "_id": "1", "_score": 1.4384103, "_source": { "content": "ssd is critical" } } ] } }
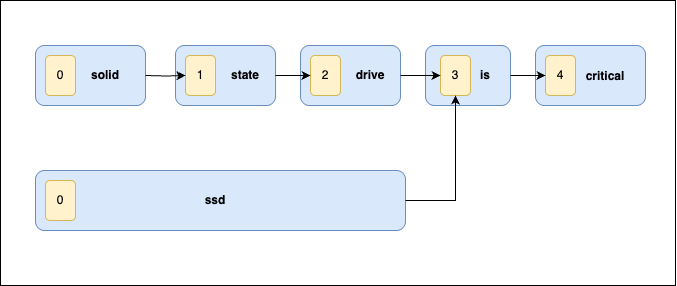
A hit occurs when using the graph-aware token filter because during the match_phrase query, an additional subquery is generated using the token graph. The following diagram illustrates the token graph created by the graph-aware token filter.