Semantic search using AWS CloudFormation and Amazon Bedrock
This tutorial shows you how to implement semantic search in Amazon OpenSearch Service using AWS CloudFormation and Amazon Bedrock. For more information, see Semantic search.
If you are using self-managed OpenSearch instead of Amazon OpenSearch Service, create a connector to the Amazon Bedrock models using the blueprints. For more information about creating a connector, see Connectors.
The CloudFormation integration automates the steps in the Semantic search using Amazon Bedrock Titan tutorials. The CloudFormation template creates an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role and invokes an AWS Lambda function to set up an AI connector and model.
Replace the placeholders beginning with the prefix your_ with your own values.
Prerequisite: Create an OpenSearch cluster
Go to the Amazon OpenSearch Service console and create an OpenSearch domain.
Note the domain Amazon Resource Name (ARN); you’ll use it in the following steps.
Step 1: Map a backend role
The OpenSearch CloudFormation template uses a Lambda function to create an AI connector with an IAM role. You must map the IAM role to ml_full_access to grant the required permissions. Follow Step 2.2 of the Semantic search using Amazon Bedrock Titan tutorial to map a backend role.
The IAM role is specified in the Lambda Invoke OpenSearch ML Commons Role Name field in the CloudFormation template. The default IAM role is LambdaInvokeOpenSearchMLCommonsRole, so you must map the arn:aws:iam::your_aws_account_id:role/LambdaInvokeOpenSearchMLCommonsRole backend role to ml_full_access.
For a broader mapping, you can grant all roles ml_full_access using a wildcard:
arn:aws:iam::your_aws_account_id:role/*
Because all_access includes more permissions than ml_full_access, mapping the backend role to all_access is also acceptable.
Step 2: Run the CloudFormation template
The CloudFormation template integration is available in the Amazon OpenSearch Service console. From the left navigation pane, select Integrations, as shown in the following image.
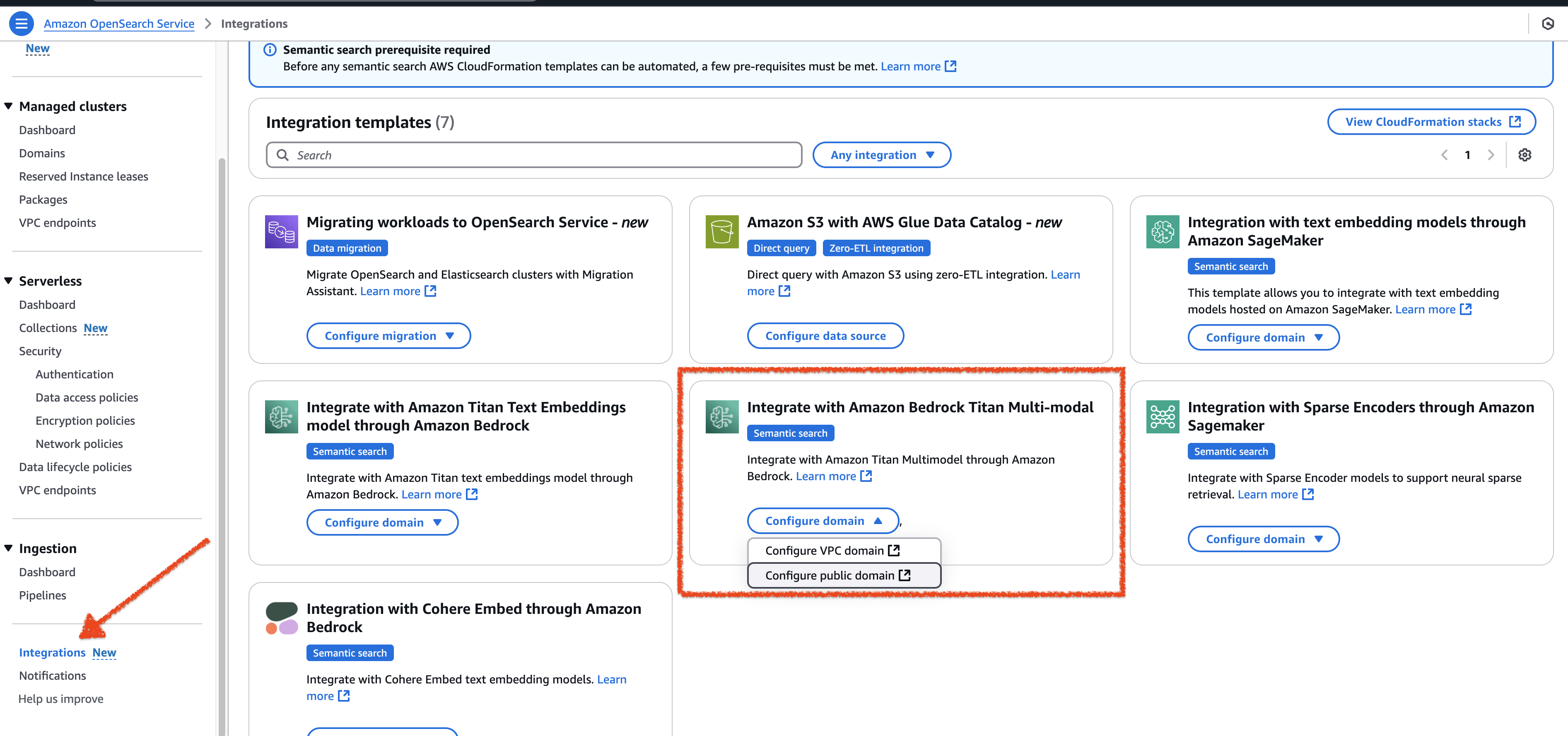
To create a connector, complete the following form.
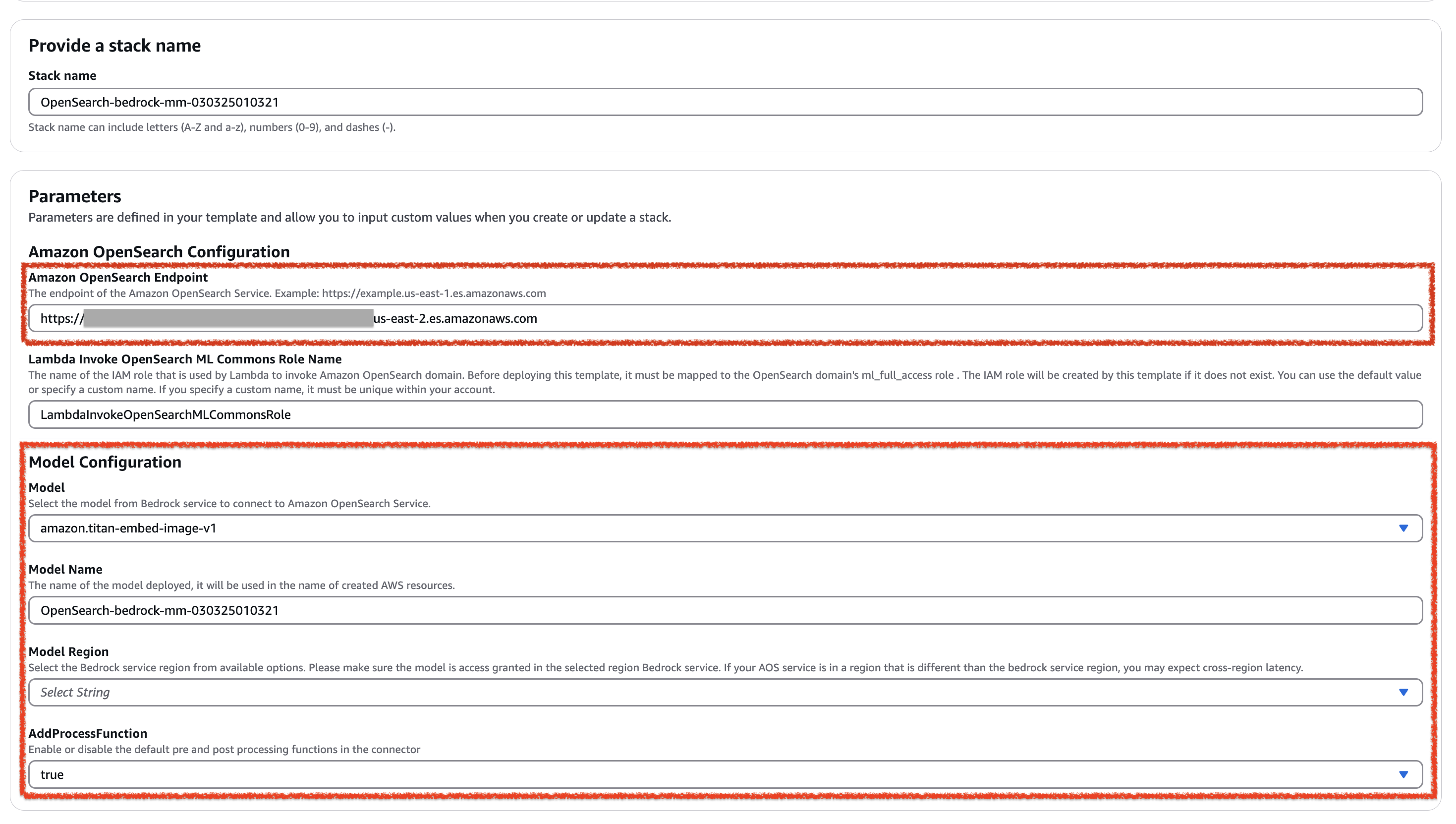
Complete the following fields, keeping all other fields at their default values:
- Enter your Amazon OpenSearch Endpoint.
- In Model Configuration, select a Model to be deployed. Choose one of the following supported models:
amazon.titan-embed-text-v1amazon.titan-embed-image-v1amazon.titan-embed-text-v2:0cohere.embed-english-v3cohere.embed-multilingual-v3
- Select a Model Region (this is the Amazon Bedrock Region).
- In AddProcessFunction, select
trueto enable orfalseto disable the default pre- and post-processing functions in the connector.
Output
After deployment, you can find the ConnectorId, the ModelId, and the BedrockEndpoint in the CloudFormation stack Outputs.
If an error occurs, follow these steps to review the logs:
- Navigate to the CloudWatch Logs section.
- Search for Log Groups that contain (or are associated with) your CloudFormation stack name.
Step 3: Configure semantic search
Follow these steps to configure semantic search.
Step 3.1: Create an ingest pipeline
First, create an ingest pipeline that uses the model on Amazon Bedrock to create embeddings from the input text:
PUT /_ingest/pipeline/my_bedrock_embedding_pipeline
{
"description": "text embedding pipeline",
"processors": [
{
"text_embedding": {
"model_id": "your_bedrock_embedding_model_id_created_in_step3",
"field_map": {
"text": "text_knn"
}
}
}
]
}
Step 3.2: Create a vector index
Next, create a vector index for storing the input text and generated embeddings:
PUT my_index
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"knn.space_type": "cosinesimil",
"default_pipeline": "my_bedrock_embedding_pipeline",
"knn": "true"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"text_knn": {
"type": "knn_vector",
"dimension": 1536
}
}
}
}
Step 3.3: Ingest data
Ingest a sample document into the index:
POST /my_index/_doc/1000001
{
"text": "hello world."
}
Step 3.4: Search the index
Run a vector search to retrieve documents from the vector index:
POST /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"neural": {
"text_knn": {
"query_text": "hello",
"model_id": "your_embedding_model_id_created_in_step4",
"k": 100
}
}
},
"size": "1",
"_source": ["text"]
}