Semantic search using a model in Amazon SageMaker
This tutorial shows you how to implement semantic search in Amazon OpenSearch Service using an embedding model in Amazon SageMaker.
If you are using self-managed OpenSearch instead of Amazon OpenSearch Service, create a connector to the model in Amazon SageMaker using the blueprint. For more information about creating a connector, see Connectors.
This tutorial does not cover how to deploy a model to Amazon SageMaker. For more information about deployment, see Real-time inference.
The easiest way to set up an embedding model in Amazon OpenSearch Service is by using AWS CloudFormation. Alternatively, you can set up an embedding model using the AIConnectorHelper notebook.
Replace the placeholders beginning with the prefix your_ with your own values.
Model input and output requirements
Ensure that the inputs for your model in Amazon SageMaker follow the format required by the default pre-processing function.
The model input must be an array of strings:
["hello world", "how are you"]
Additionally, ensure that the model output follows the format required by the default post-processing function. The model output must be an array of arrays, where each inner array corresponds to the embedding of an input string:
[
[
-0.048237994,
-0.07612697,
...
],
[
0.32621247,
0.02328475,
...
]
]
If your model input/output is not the same as the required default, you can build your own pre-/post-processing function using a Painless script.
Example: Amazon Bedrock Titan embedding model
For example, the Amazon Bedrock Titan embedding model (blueprint) input is as follows:
{ "inputText": "your_input_text" }
OpenSearch expects the following input format:
{ "text_docs": [ "your_input_text1", "your_input_text2"] }
To convert text_docs into inputText, you must define the following pre-processing function:
"pre_process_function": """
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("\"");
String first = params.text_docs[0];// Get the first doc, ml-commons will iterate all docs
builder.append(first);
builder.append("\"");
def parameters = "{" +"\"inputText\":" + builder + "}"; // This is the Bedrock Titan embedding model input
return "{" +"\"parameters\":" + parameters + "}";"""
The default Amazon Bedrock Titan embedding model output has the following format:
{
"embedding": <float_array>
}
However, OpenSearch expects the following format:
{
"name": "sentence_embedding",
"data_type": "FLOAT32",
"shape": [ <embedding_size> ],
"data": <float_array>
}
To transform the Amazon Bedrock Titan embedding model output into the format expected by OpenSearch, you must define the following post-processing function:
"post_process_function": """
def name = "sentence_embedding";
def dataType = "FLOAT32";
if (params.embedding == null || params.embedding.length == 0) {
return params.message;
}
def shape = [params.embedding.length];
def json = "{" +
"\"name\":\"" + name + "\"," +
"\"data_type\":\"" + dataType + "\"," +
"\"shape\":" + shape + "," +
"\"data\":" + params.embedding +
"}";
return json;
"""
Prerequisite: Create an OpenSearch cluster
Go to the Amazon OpenSearch Service console and create an OpenSearch domain.
Note the domain Amazon Resource Name (ARN); you’ll use it in the following steps.
Step 1: Create an IAM role to invoke the model in Amazon SageMaker
To invoke the model in Amazon SageMaker, you must create an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role with appropriate permissions. The connector will use this role to invoke the model.
Go to the IAM console, create a new IAM role named my_invoke_sagemaker_model_role, and add the following trust policy and permissions:
- Custom trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "es.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
- Permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sagemaker:InvokeEndpoint"
],
"Resource": [
"your_sagemaker_model_inference_endpoint_arn"
]
}
]
}
Note the role ARN; you’ll use it in the following steps.
Step 2: Configure an IAM role in Amazon OpenSearch Service
Follow these steps to configure an IAM role in Amazon OpenSearch Service.
Step 2.1: Create an IAM role for signing connector requests
Generate a new IAM role specifically for signing your Create Connector API request.
Create an IAM role named my_create_sagemaker_connector_role with the following trust policy and permissions:
- Custom trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "your_iam_user_arn"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
You’ll use the your_iam_user_arn IAM user to assume the role in Step 3.1.
- Permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "your_iam_role_arn_created_in_step1"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "es:ESHttpPost",
"Resource": "your_opensearch_domain_arn"
}
]
}
Note this role ARN; you’ll use it in the following steps.
Step 2.2: Map a backend role
Follow these steps to map a backend role:
- Log in to OpenSearch Dashboards and select Security on the top menu.
- Select Roles, and then select the ml_full_access role.
- On the ml_full_access role details page, select Mapped users, and then select Manage mapping.
- Enter the IAM role ARN created in Step 2.1 in the Backend roles field, as shown in the following image.
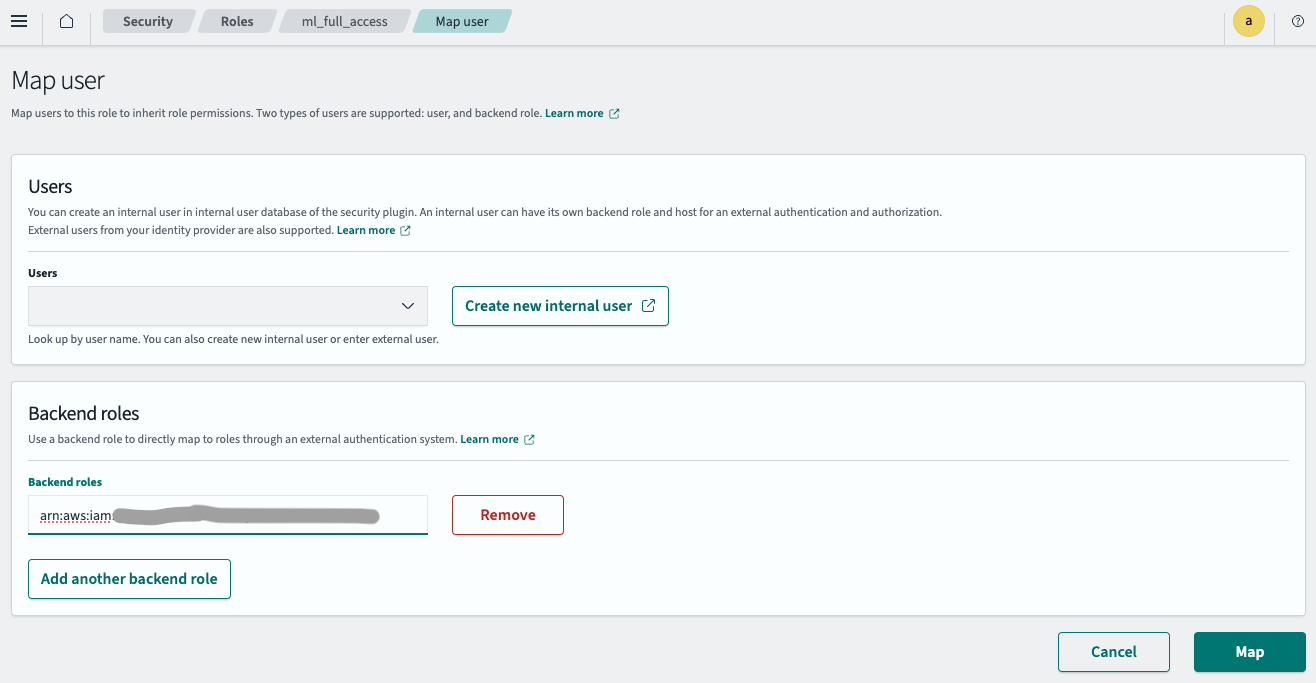
- Select Map.
The IAM role is now successfully configured in your OpenSearch cluster.
Step 3: Create a connector
Follow these steps to create a connector for the model. For more information about creating a connector, see Connectors.
Step 3.1: Get temporary credentials
Use the credentials of the IAM user specified in Step 2.1 to assume the role:
aws sts assume-role --role-arn your_iam_role_arn_created_in_step2.1 --role-session-name your_session_name
Copy the temporary credentials from the response and configure them in ~/.aws/credentials:
[default]
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your_access_key_of_role_created_in_step2.1
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your_secret_key_of_role_created_in_step2.1
AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=your_session_token_of_role_created_in_step2.1
Step 3.2: Create a connector
Run the following Python code with the temporary credentials configured in ~/.aws/credentials:
import boto3
import requests
from requests_aws4auth import AWS4Auth
host = 'your_amazon_opensearch_domain_endpoint'
region = 'your_amazon_opensearch_domain_region'
service = 'es'
credentials = boto3.Session().get_credentials()
awsauth = AWS4Auth(credentials.access_key, credentials.secret_key, region, service, session_token=credentials.token)
path = '/_plugins/_ml/connectors/_create'
url = host + path
payload = {
"name": "Sagemaker embedding model connector",
"description": "Connector for my Sagemaker embedding model",
"version": "1.0",
"protocol": "aws_sigv4",
"credential": {
"roleArn": "your_iam_role_arn_created_in_step1"
},
"parameters": {
"region": "your_sagemaker_model_region",
"service_name": "sagemaker"
},
"actions": [
{
"action_type": "predict",
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"content-type": "application/json"
},
"url": "your_sagemaker_model_inference_endpoint",
"request_body": "${parameters.input}",
"pre_process_function": "connector.pre_process.default.embedding",
"post_process_function": "connector.post_process.default.embedding"
}
]
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
r = requests.post(url, auth=awsauth, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(r.status_code)
print(r.text)
The script outputs a connector ID:
{"connector_id":"tZ09Qo0BWbTmLN9FM44V"}
Note the connector ID; you’ll use it in the next step.
Step 4: Create and test the model
Log in to OpenSearch Dashboards, open the DevTools console, and run the following requests to create and test the model.
-
Create a model group:
POST /_plugins/_ml/model_groups/_register { "name": "Sagemaker_embedding_model", "description": "Test model group for Sagemaker embedding model" }The response contains the model group ID:
{ "model_group_id": "MhU3Qo0BTaDH9c7tKBfR", "status": "CREATED" } -
Register the model:
POST /_plugins/_ml/models/_register { "name": "Sagemaker embedding model", "function_name": "remote", "description": "test embedding model", "model_group_id": "MhU3Qo0BTaDH9c7tKBfR", "connector_id": "tZ09Qo0BWbTmLN9FM44V" }The response contains the model ID:
{ "task_id": "NhU9Qo0BTaDH9c7t0xft", "status": "CREATED", "model_id": "NxU9Qo0BTaDH9c7t1Bca" } -
Deploy the model:
POST /_plugins/_ml/models/NxU9Qo0BTaDH9c7t1Bca/_deployThe response contains a task ID for the deployment operation:
{ "task_id": "MxU4Qo0BTaDH9c7tJxde", "task_type": "DEPLOY_MODEL", "status": "COMPLETED" } -
Test the model:
POST /_plugins/_ml/models/NxU9Qo0BTaDH9c7t1Bca/_predict { "parameters": { "input": ["hello world", "how are you"] } }The response contains the embeddings generated by the model:
{ "inference_results": [ { "output": [ { "name": "sentence_embedding", "data_type": "FLOAT32", "shape": [ 384 ], "data": [ -0.034477264, 0.031023195, 0.0067349933, ...] }, { "name": "sentence_embedding", "data_type": "FLOAT32", "shape": [ 384 ], "data": [ -0.031369038, 0.037830487, 0.07630822, ...] } ], "status_code": 200 } ] }
Step 5: Configure semantic search
Follow these steps to configure semantic search.
Step 5.1: Create an ingest pipeline
First, create an ingest pipeline that uses the model in Amazon SageMaker to create embeddings from the input text:
PUT /_ingest/pipeline/my_sagemaker_embedding_pipeline
{
"description": "text embedding pipeline",
"processors": [
{
"text_embedding": {
"model_id": "your_sagemaker_embedding_model_id_created_in_step4",
"field_map": {
"text": "text_knn"
}
}
}
]
}
Step 5.2: Create a vector index
Next, create a vector index for storing the input text and generated embeddings:
PUT my_index
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"knn.space_type": "cosinesimil",
"default_pipeline": "my_sagemaker_embedding_pipeline",
"knn": "true"
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"text_knn": {
"type": "knn_vector",
"dimension": your_sagemake_model_embedding_dimension
}
}
}
}
Step 5.3: Ingest data
Ingest a sample document into the index:
POST /my_index/_doc/1000001
{
"text": "hello world."
}
Step 5.4: Search the index
Run a vector search to retrieve documents from the vector index:
POST /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"neural": {
"text_knn": {
"query_text": "hello",
"model_id": "your_embedding_model_id_created_in_step4",
"k": 100
}
}
},
"size": "1",
"_source": ["text"]
}